Lambda Expressions
The lambda operator or lambda function is a way to create small anonymous functions, i.e. functions without a name. These functions are throw-away functions, i.e. they are just needed where they have been created.
Lambda functions are mainly used in combination with the functions filter(), map() and reduce()(reduce() is no more supported in Python 3.x).
The general syntax of a lambda function is quite simple: lambda <argument_list> : <expression>
The argument list consists of a comma separated list of arguments and the expression is an arithmetic expression using these arguments.
The following example of a lambda function returns the sum of its two arguments:
sum = lambda x,y : x + y
sum(3,4)
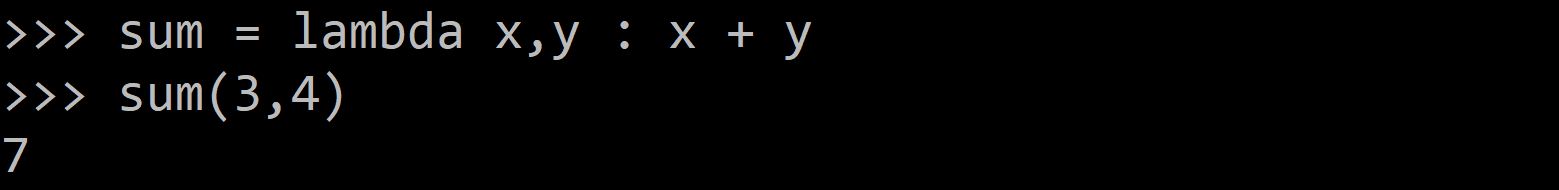
We could have had the same effect by just using the following conventional function definition:
def sum(x,y):
return x+y
sum(3,4)

Map() function
The advantage of the lambda operator can be seen when it is used in combination with the map() function.
map() is a function with two arguments:

The first argument func is the name of a function and the second a sequence (e.g. a list) seq. map() applies the function func to all the elements of the sequence seq. It returns a new list with the elements changed by func.
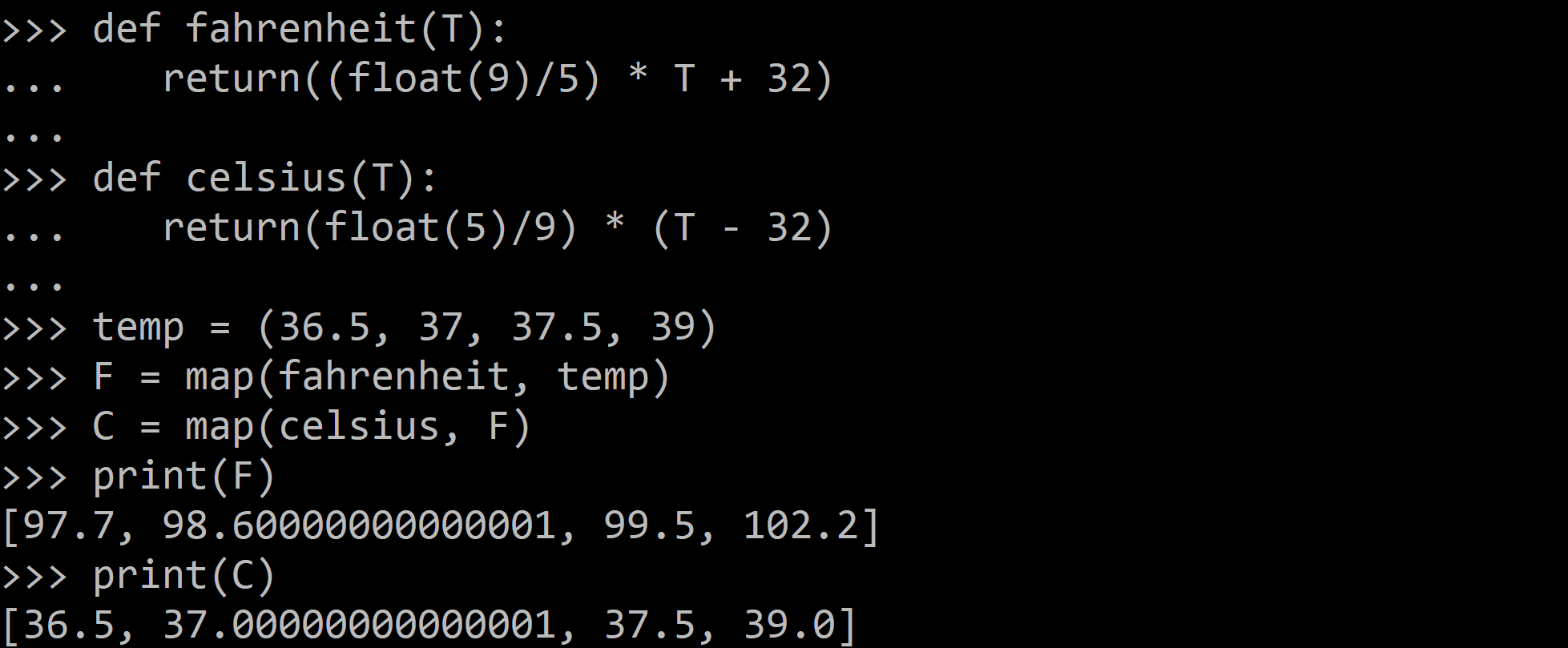
The below example of the map() function doesn’t use lambda. By using lambda, we wouldn't have had to define and name the functions fahrenheit() and celsius().
def fahrenheit(T):
return((float(9)/5) * T + 32)
def celsius(T):
return(float(5)/9) * (T - 32)
temp = (36.5, 37, 37.5, 39)
F = map(fahrenheit, temp)
C = map(celsius, F)
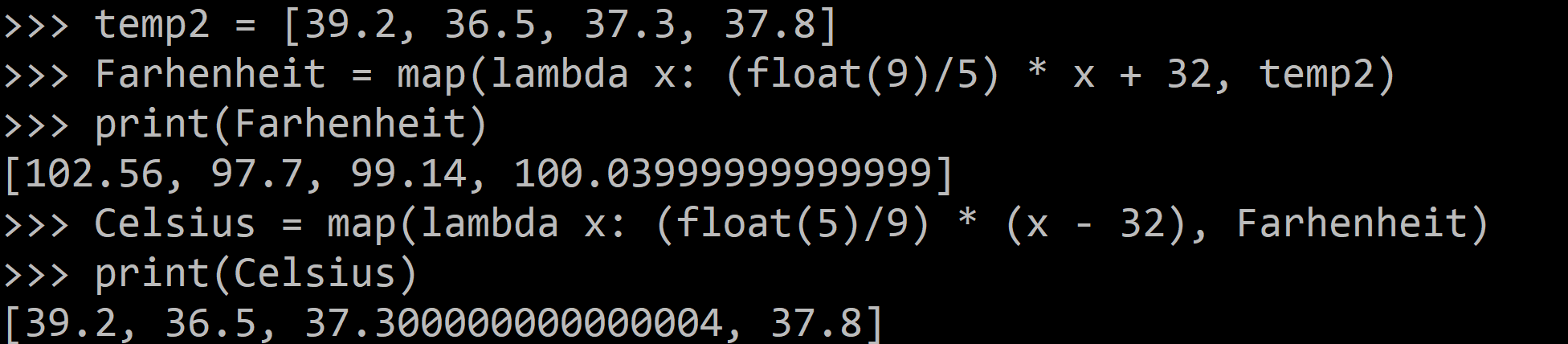
The below example of the map() function use lambda:
temp2 = [39.2, 36.5, 37.3, 37.8]
Farhenheit = map(lambda x: (float(9)/5) * x + 32, temp2)
print(Farhenheit)
Celsius = map(lambda x: (float(5)/9) * (x - 32), Farhenheit)
print(Celsius)
map() can be applied to more than one list but the lists have to have the same length.
map() will apply its lambda function to the elements of the argument lists, i.e. it first applies to the elements with the 0th index, then to the elements with the 1st index until the n-th index is reached.
a = [1,2,3,4]
b = [17,12,11,10]
c = [-1,-4,5,9]
map(lambda x,y: x+y, a,b)
map(lambda x,y,z: x+y+z, a,b,c)
map(lambda x,y,z: x+y-z, a,b,c)

Reduce() function
The function reduce (func, seq) continually applies the function func() to the sequence seq. It returns a single value.
If seq= [ s1, s2, s3, ... , sn ], calling reduce(func,seq) works like this:
- At first the first two elements of seq will be applied to func, i.e. func(s1,s2). The list on which reduce() works looks now like this: [func(s1, s2), s3, ... ,sn]
- In the next step func will be applied on the previous result and the third element of the list, i.e. func(func(s1, s2),s3). The list looks like this now: [func(func(s1, s2),s3), ... ,sn]
- Continue like this until just one element is left and return this element as the result of reduce()
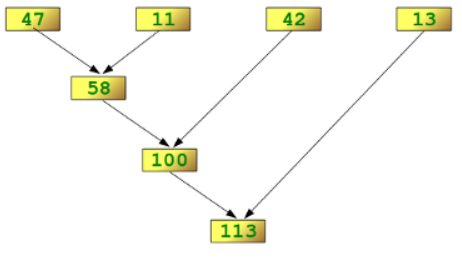
We illustrate this process in the following example:
reduce(lambda x,y: x+y, [47,11,42,13])

The following diagram shows the intermediate steps of the calculation:
Exercise Lambda functions
Imagine an accounting routine used in a book shop. It works on a list with sublists, which look like this:
| Order Number | Book Title and Author | Quantity | Price per Item |
|---|---|---|---|
| 34587 | Learning Python, Mark Lutz | 4 | 40.95 |
| 98762 | Programming Python, Mark Lutz | 5 | 56.80 |
| 77226 | Head First Python, Paul Barry | 3 | 32.95 |
| 88112 | Einführung in Python3, Bernd Klein | 3 | 24.99 |
In the Python shell, write a Python program that computes the sum of all products of the price per items and the quantity (price per item x quantity). To enter the Python shell, open the terminal and type python. Use map and reduce function to do so.
You can write the list with sublists like the following in the Python shell:orders = [ ["34587", "Learning Python, Mark Lutz", 4, 40.95], ["98762", "Programming Python, Mark Lutz", 5, 56.80], ["77226", "Head First Python, Paul Barry", 3, 32.95], ["88112", "Einfuhrung in Python3, Bernd Klein", 3, 24.99]]The result should be: 621.62
Hints:
• The input of a reduce() can be the output of a map(), but this is not mandatory.Write a Python program, which returns a list with 2-tuples. Each tuple consists of the order number and the product of the price per items and the quantity. The product should be increased by $10 if the value of the order is less than $100.00. Write a Python program using lambda and map.
The output of your program should look like this:
[('34587', 163.8), ('98762', 284.0), ('77226', 108.85000000000001), ('88112', 84.97)]Hints:
• You can write an IF … ELSE condition in a lambda function.
• The input of a map() can be the output of another map().